
“These images are going to remind the world that America can do big things and remind the American people – especially our children – that there’s nothing beyond our capacity,” President Biden said at the launch. “We can see possibilities no one has ever seen before. We can go places no one has ever gone before.”
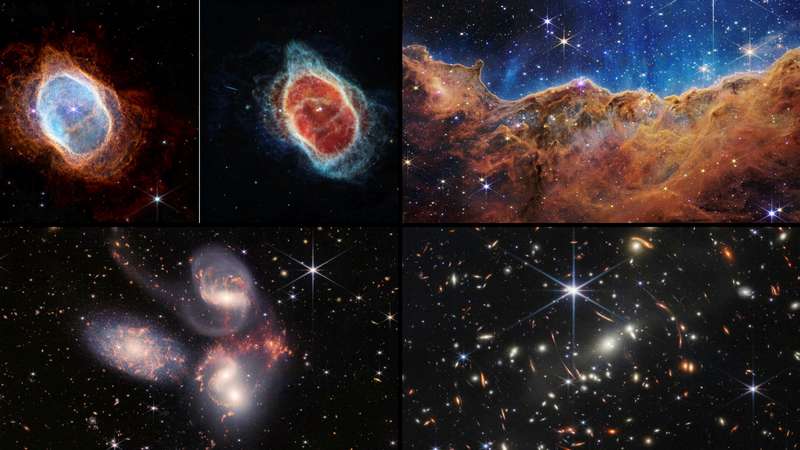
The rare pictures of the Carina Nebula showed a mountain and valley of stars. According to NASA, the “three-dimensional picture looks like craggy mountains on a moonlit evening.” It added that the highest parts “in [the] image are about 7 light-years high.”
With this new image of the Carina Nebula, astrologers now understand better the birth and life of new stars.
“Up to this point, scientists have had very little data about the influence of the multitude of young and more energetic low-mass stars. With Webb, they will be able to obtain a full census of their number and impact throughout the nebula,” NASA said on its website.
The new images also reveal more about Stephan’s Quintet. Stephan’s Quintet is a visual grouping of five galaxies. Although there was previous knowledge of five galaxies, NASA said: “The information from Webb provides new insights into how galactic interactions may have driven galaxy evolution in the early universe.”
The closest of the five galaxies is about 40 million light years away from the earth, while the remaining four are about 290 million light-years away. The study of these relative nearby galaxies will help scientists better understand structures seen in a much more distant universe.
The new images also include pictures of the Southern Ring Nebular. NASA said the rare picture of the Southern Ring Nebular shows that “some stars save the best for last.”The image includes “two stars, which are locked in a tight orbit, shape the local landscape.” It was the first time scientists realized that the dying stars were cloaked in dust.
According to NASA, “Each shell the star puffed off gives researchers the ability to precisely measure the gas and dust that are present within it.”
Another image released “shows evidence of haze and clouds that previous studies of this planet did not detect.” The picture hinted that there could be habitable planets apart from the earth.
Finally, the images released include one which shows the farthest point ever captured in the Universe.
NASA administrator Bill Nelson said it was the deepest and sharpest infrared image of the distant universe. He described it as a tiny sliver of the vast universe.
“Webb’s First Deep Field is not only the first full-color image from the James Webb Space Telescope, it’s the deepest and sharpest infrared image of the distant universe, so far. This image covers a patch of sky approximately the size of a grain of sand held at arm’s length. It’s just a tiny sliver of the vast universe,” Bill Nelson said.
“This mission was made possible by human ingenuity – the incredible NASA Webb team and our international partners at the European Space Agency and the Canadian Space Agency. Webb is just the start of what we can accomplish in the future when we work together for the benefit of humanity,” he added.
The recent images are a clear indication of the ability of the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST). It is the largest optical telescope in space. Its sensitivity and improved infrared resolution make it easy to capture images that are too old, faint, or distant for other telescopes.
Scientists have said these new images and others to be captured by the Telescope in the future will help to deepen the knowledge of outer space.











0 Comments